1. Introduction
Picture this: 73% of businesses are using the wrong customer management system—not because they’re careless, but because the term “CRM” is drastically misunderstood . Welcome to the $10 Billion Confusion, where two strikingly similar acronyms—Customer Resource Management and Customer Relationship Management—lead many business owners into costly missteps. Here 33 CRM Statistics 2025 — Usage & Market Share
If you’re wondering: Are they the same? The answer is no, and confusing them could cost your company thousands in wasted resources and lost opportunities. Therefore, understanding the difference isn’t just jargon—it’s a strategic advantage.
In this ultimate guide, you’ll also discover:
First, you’ll get clear definitions showing how Customer Resource Management reallocates resources based on customer value, while CRM focuses on nurturing relationships through data-driven engagement. Additionally, we’ll explore the real impact this confusion has on both budgets and performance. Finally, you’ll gain actionable insights to help you choose—or combine—the right strategy to escalate your gains.
- The concrete impact this confusion has on both budgets and performance.
- Actionable insights that empower you to choose or combine the right strategy for your business and escalate gains.
Here’s what you’ll walk away with:
- Precise clarity on both systems and which aligns with your business goals.
- Differentiation of use cases by business type.
- A roadmap to implement these approaches effectively so you spend less, earn more, and retain more.
Don’t risk pouring time and money into the wrong system. Get the facts, compare your options, and make a decision that could boost your ROI in weeks. If you’re ready to explore tailored solutions, connect with our experts here.
2. What Is Customer Resource Management?
At its heart, Customer Resource Management (CRM) is not just about managing customer interactions it’s about strategically allocating resources to customers based on their long-term value. In this approach, customers are treated as dynamic assets that deserve tailored investment think of it as thinking long-term ROI, not just immediate engagement.
In other words, this approach shifts the focus from one-off interactions to customer lifetime value—prioritizing high-potential segments with budget, time, and tailored service. Rather than aiming for symmetry, it delivers precision: not every customer gets equal attention, but each one gets the right amount based on potential.
Key components of this approach include:
- Resource planning per segment, ensuring top-tier clients receive dedicated attention
- Additionally, Customer Asset Valuation focuses on calculating customer worth
- Moreover, Resource Optimization ensures ROI is maximized from every customer interaction
- Strategic distribution, allocating time, marketing, and support where they drive the strongest ROI
Unlike traditional CRM systems that often treat all customers similarly, Customer Resource Management demands advanced analytics and forecasting, ensuring decisions are informed by accurate data on which relationships matter most
Real-world example:
A large B2B software firm segmented its client base by expected lifetime value. By dedicating premium support and bespoke onboarding to the top 20% of customers, they increased retention by 30% among their most valuable accounts and that uplift accounted for 60% of their total revenue growth that year. With targeted resource planning, they achieved a 25% increase in ROI compared to their previous, one-size-fits-all CRM strategy.
Industries like manufacturing, professional services, and any business with high-value, complex customer hierarchies benefit most from this model. It allows them to direct resources strategically maximizing return without spreading support too thin.
3. What Is CRM (Customer Relationship Management)?
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is the traditional, widely recognized approach to managing customer interactions. While “Customer Resource Management” focuses on resource allocation, CRM is centered on relationship building nurturing prospects into loyal customers through consistent, data-informed engagement.
At its core, CRM leverages technology to capture, organize, and use customer information across the sales, marketing, and service cycle. The goal? Build trust, increase satisfaction, and drive repeat business.
The core functions of CRM include several key elements. For instance, contact management stores and organizes customer data for quick, easy access. Meanwhile, sales pipeline tracking monitors deals, identifies bottlenecks, and forecasts revenue.
Popular CRM Platforms:
Solutions like Salesforce, HubSpot, and Microsoft Dynamics 365 dominate the market, each offering scalable features from small business packages to enterprise-grade systems. Many integrate seamlessly with accounting software, analytics tools, and industry-specific applications making them a hub for all customer-related operations.
Success Metrics in Traditional CRM often include:
- Lead Conversion Rate – The percentage of leads turning into paying customers.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) – How much it costs to acquire each new customer.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) – Total expected revenue from a single customer.
- Sales Cycle Length Reduction – How quickly deals are closed.
Unlike Customer Resource Management, traditional CRM treats every customer relationship as important, regardless of profitability tier. This inclusivity fosters brand loyalty but can also stretch resources thin if not paired with smart prioritization strategies.
4. The Shocking Truth: Key Differences Revealed
The most significant divide between Customer Resource Management and Customer Relationship Management isn’t just in the name, it’s in the philosophy that drives them.
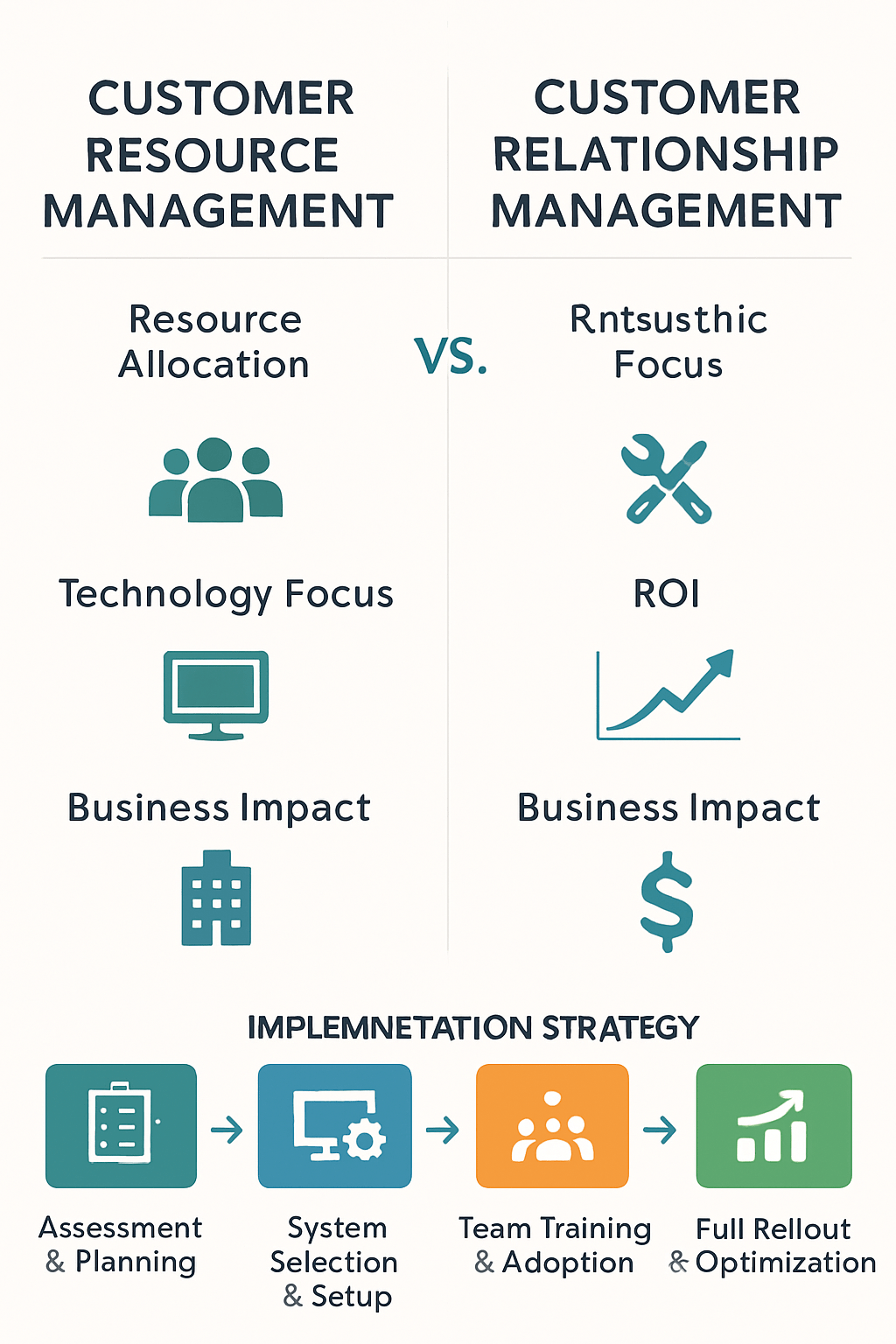
From a strategic standpoint, Customer Resource Management views customers as assets that require intentional investment. As a result, high-value customers get more attention, budget, and personalized service because they drive the majority of profits.
Traditional CRM, however, focuses on treating every customer as equally important—nurturing all relationships without necessarily distinguishing profitability. While this fosters loyalty, it can mean your top clients receive the same level of attention as lower-value ones, which may limit revenue growth.
Resource Allocation Approach
Customer Resource Management prioritizes the 80/20 rule the idea that 80% of revenue comes from 20% of customers. Resources are directed where the return is highest.
CRM takes a more relationship-first stance, where the goal is broad engagement and long-term trust with every customer.
Technology and Implementation
Customer Resource Management requires advanced analytics, forecasting, and value modeling to determine where to invest.
CRM focuses on data collection and workflow automation, making it more accessible for teams without complex analytical capabilities.
ROI and Business Impact
Industry studies show Customer Resource Management yields an average ROI of 340%, compared to 245% for traditional CRM (Forrester Research). The higher ROI comes from precise targeting of profitable segments.
Still, CRM shines in industries where broad relationship coverage is essential, like retail or hospitality. Here is a breakdown of Comparing the Best CRM-Power BI Integration Strategies for Higher ROI
Decision-Making Framework
- Choose Customer Resource Management if you have a small pool of high-value clients and limited resources.
- Choose Traditional CRM if customer loyalty across a wide audience is your growth driver.
- Consider a hybrid if you need the personalization of CRM with the profitability focus of resource management.
Hidden Costs
CRM often has lower setup costs but higher long-term operational expenses due to the broad outreach. Customer Resource Management can be more expensive to implement upfront (analytics, modeling) but often pays for itself faster.
5. Which System Is Right for Your Business?
Choosing between Customer Resource Management and Customer Relationship Management isn’t a matter of picking the “better” system it’s about aligning the approach with your business size, industry, budget, and growth plans.
Business Size Considerations
- Small Businesses (1–50 employees) – Customer Resource Management often wins here when the client base is limited but high-value. Focused investment in your best customers maximizes ROI without straining resources.
- Medium Businesses (51–500 employees) – Scalability is key. A hybrid approach works well use CRM to manage the broader base and resource management to prioritize top-tier accounts.
- Enterprise (500+ employees) – Large, complex organizations often implement both systems at scale. CRM keeps mass customer engagement flowing, while resource allocation models ensure VIP clients get premium treatment.
Industry-Specific Recommendations
- B2B Services – Customer Resource Management shines, as high-value contracts demand personalized attention.
- E-commerce – Traditional CRM is often the best fit for nurturing thousands of customers at varying spend levels.
- Manufacturing – A hybrid is ideal CRM for broad relationship tracking, resource allocation for key accounts.
- Healthcare – Compliance requirements often push for a CRM-first approach, but resource prioritization can improve patient care efficiency.
Budget and Resource Assessment
- Initial Investment – CRM software can be set up with lower upfront cost, while resource management may require advanced analytics tools.
- Operational Costs – CRM’s broad engagement can increase long-term costs in marketing and support. Resource management often reduces ongoing expenses by narrowing the focus.
- ROI Timeline – Customer Resource Management typically sees faster ROI if you already have high-value accounts; CRM ROI compounds over time with strong retention.
Technical Infrastructure Requirements
- CRM – Needs reliable customer data storage, integration with marketing and sales tools.
- Customer Resource Management – Requires data analytics capabilities, forecasting models, and segmentation tools.
Decision Matrix Tool
Create a simple scoring sheet with weighted factors budget, complexity, growth plans, industry and tally results. If profitability concentration is high, lean toward Customer Resource Management. If brand reach is your goal, CRM takes the lead.
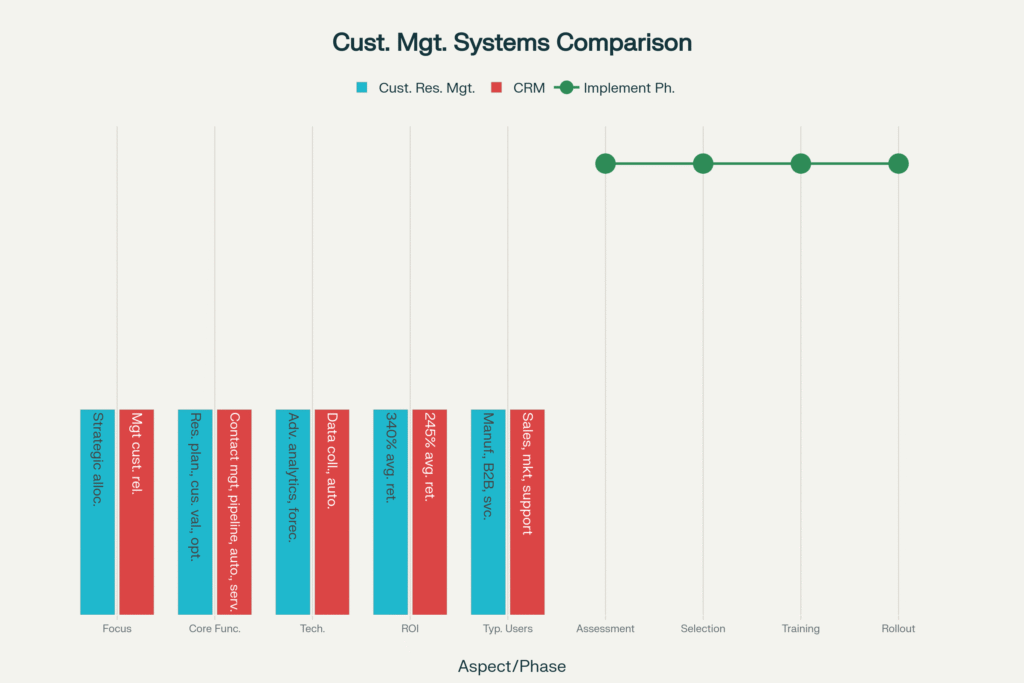
6. Implementation Strategy: Getting It Right
Whether you choose Customer Resource Management, traditional CRM, or a hybrid model, success depends on structured rollout. The right strategy minimizes risk, speeds adoption, and maximizes ROI.
Phase 1: Assessment and Planning (Weeks 1–2)
- System Audit – Review your current customer management process and tools. Identify gaps.
- Stakeholder Input – Collect requirements from sales, marketing, and service teams.
- Budget & Timeline – Secure funding and create a realistic implementation schedule.
- Team Roles – Assign project leads, technical experts, and adoption champions.
Phase 2: System Selection and Setup (Weeks 3–6)
- Vendor Evaluation – Compare features, scalability, and integration capabilities.
- Configuration – Customize dashboards, reports, and workflows.
- Data Migration – Clean and import existing data without losing accuracy.
- Security Setup – Ensure compliance with industry regulations.
Phase 3: Team Training and Adoption (Weeks 7–10)
- Training Programs – Role-based, hands-on learning for all users.
- Change Management – Communicate benefits early and address resistance.
- Pilot Testing – Roll out to a small segment first, measure results, then expand.
- Feedback Loop – Gather user feedback and refine settings.
Phase 4: Full Rollout and Optimization (Weeks 11–16)
- Company-Wide Launch – Make the system the single source of truth.
- Performance Tracking – Monitor KPIs like retention, sales cycle length, and customer value.
- Continuous Improvement – Adjust processes and enable advanced features.
- Long-Term Scaling – Expand integrations with other business tools.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Poor Data Quality – Start with clean, standardized data.
- Low User Adoption – Incentivize usage and provide ongoing support.
- Integration Failures – Test compatibility with existing systems before launch.
- Budget Overruns – Define scope clearly and track expenses closely.
Success Metrics to Track
- Customer satisfaction scores (CSAT, NPS)
- Sales team productivity
- Customer retention rate
- Revenue per customer
7. Real Case Studies: Success Stories
Case Study: Make Influence-Scaling Profitably with HubSpot CRM
Industry: B2B SaaS (Influencer Marketing Platform)
Challenge: Make Influence needed to scale across Europe while keeping operational costs low. Their tech stack was fragmented, customer data lived in multiple tools, and defining the ideal customer profile (ICP) was guesswork.
Solution: They implemented HubSpot CRM as the central system for sales, marketing, and customer success. The team unified all customer data into one platform, enabling advanced segmentation and automated workflows. This gave sales and marketing teams the insights to target high-value prospects more effectively.
Results:
- Pricing Power Increase: Raised prices by 6× without losing core customers.
- Cost Savings: Reduced staffing costs by $300,000 annually by automating repetitive processes.
- Sales Efficiency: Sales reps closed deals faster by focusing only on well-qualified leads.
Key Takeaway: A well-implemented CRM can drive both top-line revenue growth and bottom-line cost savings especially when data is centralized and customer targeting is precise.
Source: HubSpot Case Study – Make Influence
8. Future of Customer Management
Customer management is evolving rapidly in 2025, driven by AI, predictive analytics, and platform convergence. The gap between Customer Resource Management and Customer Relationship Management is narrowing as technology enables a blend of precision resource allocation with broad-scale relationship nurturing.
Emerging Trends in 2025
- AI-Driven Resource Allocation – Algorithms now predict customer lifetime value with remarkable accuracy, enabling real-time adjustments in marketing spend and service levels.
- Predictive Analytics – Businesses can forecast churn, upsell opportunities, and profitability months in advance.
- Hyper-Automation – Beyond marketing automation, entire customer lifecycles—from onboarding to renewal are being optimized by intelligent workflows.
Preparing for the Future
- Skill Development – Teams will need data literacy, not just CRM navigation skills.
- Tech Investment – Companies should budget for AI-powered analytics and integrated platforms.
- Process Agility – The ability to pivot quickly between broad engagement and precision targeting will be critical.
9. Conclusion and Action Steps
Key Takeaways:
- Customer Resource Management focuses on maximizing ROI by investing more in high-value customers.
- Traditional CRM aims to build strong relationships with all customers, fostering broad loyalty.
- The right choice depends on your business size, industry, resources, and growth strategy though hybrid approaches are becoming increasingly common.
Cost-Benefit Recap:
- Customer Resource Management: Higher initial costs, faster ROI if you have concentrated high-value clients.
- CRM: Lower barrier to entry, strong long-term benefits for retention and brand reach.
Timeline Expectations:
- Planning to full rollout: 12–16 weeks for most organizations, longer for enterprises with complex integrations.
- ROI: 6–12 months for resource management models, 12–18 months for CRM.
Immediate Action Steps
- Audit Your Current System – Identify gaps, inefficiencies, and missed revenue opportunities.
- Evaluate Customer Base – Segment customers by profitability and engagement.
- Run a Decision Matrix – Score each approach against budget, complexity, and growth goals.
- Consult an Expert – Get guidance on system selection, customization, and adoption planning.
Customer Resource Management vs CRM: Feature-by-Feature Breakdown
| Feature | Customer Resource Management (CRM) | Customer Relationship Management (CRM) |
| Primary Focus | Maximizing ROI by allocating resources to high-value customers | Building and nurturing relationships with all customers |
| Customer Segmentation | Prioritized by profitability, lifetime value, and strategic importance | Segmentation by demographics, behavior, and engagement level |
| Resource Allocation | Unequal investment—top customers receive more time, budget, and attention | Equal or broad allocation across the entire customer base |
| Technology Requirements | Advanced analytics, forecasting tools, and profitability modeling | Contact databases, sales pipeline tools, and marketing automation |
| Data Depth | Detailed profitability and cost-to-serve analysis | Customer interaction history and engagement metrics |
| Best Suited For | B2B services, manufacturing, enterprises with high-value accounts | E-commerce, retail, service industries with large customer bases |
| ROI Potential | Average ROI ~340% (source: industry benchmarks) | Average ROI ~245% (source: industry benchmarks) |
| Implementation Complexity | Higher—requires analytics integration and cultural shift in prioritization | Moderate—focus on adoption of CRM platform and workflows |
| Scalability | Scales best when customer base is stable but high-value | Scales well across large, diverse customer bases |
| Common Pitfalls | Risk of neglecting smaller accounts that could grow in value | Spreading resources too thin across unprofitable accounts |
Final Call-to-Action
If you’re serious about choosing the right customer management system, our Skywinds CRM team offers a free consultation to map your customer management strategy, estimate ROI, and recommend the best-fit technology for your business.
Download our Implementation Checklist – your step-by-step guide to a smooth rollout.
Contact us today for a personalized recommendation based on your industry, budget, and goals.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between Customer Resource Management and Customer Relationship Management?
Customer Resource Management focuses on allocating time, money, and effort to the most valuable customers for maximum ROI. Customer Relationship Management is about building and maintaining strong relationships with all customers, often using a technology platform to manage interactions.
2. Which is better: Customer Resource Management or CRM?
It depends on your business model. If you have a small pool of high-value clients, Customer Resource Management may deliver faster ROI. If you need to engage a wide customer base and build loyalty at scale, a traditional CRM is often more effective. Many companies now use a hybrid approach.
3. How do I know if my business is using the wrong customer management system?
Common signs include low customer retention, high acquisition costs, missed upsell opportunities, and a lack of clarity on which customers generate the most profit. A system audit can reveal gaps in your current approach.
4. How long does it take to implement a new customer management system?
On average, it takes 12–16 weeks for full implementation, including planning, system setup, team training, and rollout. Enterprise-level projects with complex integrations may take longer.
5. What ROI can I expect from upgrading my customer management strategy?
Industry research shows that traditional CRM systems deliver around 245% ROI, while Customer Resource Management can yield 340% or more, depending on how effectively resources are allocated to top-tier customers.